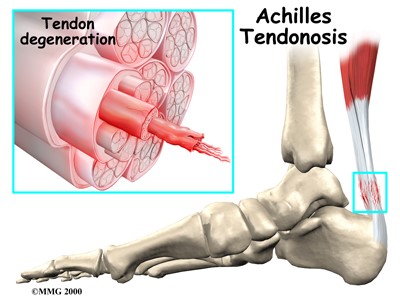
Achilles tendinopathy is a common overuse injury that is characterised by pain and stiffness around the Achilles tendon with loss of function in activities such as walking, running and jumping. It occurs both in sedentary and athletic populations, with a lifetime prevalence of 52% in middle and long-distance runners, and 6% in the general population. They generally develop gradually, although pain may present quite suddenly after a sudden increase in loading.
Tendon injuries exist on a continuum and can either be acute and short-lived or when poorly managed, become chronic and degenerative, resulting in weakness of the tendon with more persistent pain and dysfunction. Achilles tendinopathy can be either in the mid-portion of the Achilles tendon, or in the insertion of the Achilles on the calcaneus (heel).
Risk Factors
Several factors have been proposed to contribute to Achilles tendinopathy, including:
- Sudden increases in training volume or intensity.
- Walking, running and jumping are often risk factors due to the high levels of strain and repeated loading through the Achilles in these activities.
- Poor footwear choice or a change of footwear may cause overload.
- Poor running or lower limb biomechanics.
- The use of fluroquinolone antibiotics.
- Decreased calf or lower limb strength.
- Poor biomechanics.
Diagnosis
The diagnosis of Achilles tendinopathy by an experienced Physiotherapist is quite straight forward and while imaging can be performed it is generally unnecessary.
- There is often an increase in loading in the history, leading up to onset of the condition.
- Achilles injuries often have quite a characteristic behaviour over the day. They will often be quite sore in the morning, then warm up to a degree and may or may not worsen as the day progresses.
- The tendon is quite superficial, and palpation of the tendon will generally reproduce symptoms.
- At certain stages of an Achilles tendinopathy there may be a visible bump in the middle of the tendon.
- Testing which loads the tendon should be able to reproduce pain.
Management
Management of Achilles tendinopathy is a multimodal approach that should be based on the assessment findings. Common management strategies include:
- Education around the causes and management of tendinopathy.
- Activity modification to reduce loading on the Achilles such as decreasing run distances or tracking daily step count.
- Graduated loading of the tendon with strength training and a slow progression back to explosive movements such as running.
- Correction of any abnormal biomechanics.
- Changes in footwear to a higher heel drop or insertion of heel lifts may help shift load away from the Achilles tendon either short or long-term.
- Other adjuncts may include manual therapy, ice, pain medication or injections in some cases.
While a very common and often disabling condition, with a concerted effort on rehabilitation and a shared decision making process between the client and physiotherapist, a significant improvement in symptoms and function should be possible.
If you are putting up with Achilles tendinopathy, book now with one of our experienced physiotherapists to create a plan to get you back In Balance and doing the things you love!